
本文摘录自《设计模式就该这样学》
1 关于产品等级结构和产品族
在讲解具象鞋厂之前,我们要了解两个概念:产品等级结构和产品族,如下图所示。
上图中有正方形、圆形和矩形3种图形,相同颜色、相同深浅的代表同一个产品族,相同形状的代表同一个产品等级结构。同样可以从生活中来举例,比如,美的电器生产多种家用电器,那么上图中,颜色最深的正方形就代表美的洗衣机,颜色最深的方形代表美的空调,颜色最深的矩形代表美的热水器,颜色最深的一排都属于美的品牌,都属于美的电器这个产品族。再看最右边的矩形,颜色最深的被指定了代表美的热水器,那么第二排颜色稍为浅一点的矩形代表海尔热水器。同理,同一产品族下还有格力洗衣机、格力空调、格力热水器。
再看右图,最左边的小房子被觉得是具体的鞋厂,有美的鞋厂、海信鞋厂、格力鞋厂。每个品牌的鞋厂都生产洗衣机、空调和热水器。
通过前面两张图的对比理解,相信你们对具象鞋厂有了十分形象的理解。
2 抽象鞋厂模式的通用写法
以下是具象鞋厂模式的通用写法。
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IFactory factory = new ConcreteFactoryA();
factory.makeProductA();
factory.makeProductB();
factory = new ConcreteFactoryB();
factory.makeProductA();
factory.makeProductB();
}
//抽象工厂类
public interface IFactory {
IProductA makeProductA();
IProductB makeProductB();
}
//产品A抽象
public interface IProductA {
void doA();
}
//产品B抽象
public interface IProductB {
void doB();
}
//产品族A的具体产品A
static class ConcreteProductAWithFamilyA implements IProductA{
public void doA() {
System.out.println("The ProductA be part of FamilyA");
}
}
//产品族A的具体产品B
static class ConcreteProductBWithFamilyA implements IProductB{
public void doB() {
System.out.println("The ProductB be part of FamilyA");
}
}
//产品族B的具体产品A
static class ConcreteProductAWithFamilyB implements IProductA{
public void doA() {
System.out.println("The ProductA be part of FamilyB");
}
}
//产品族B的具体产品B
static class ConcreteProductBWithFamilyB implements IProductB{
public void doB() {
System.out.println("The ProductB be part of FamilyB");
}
}
//具体工厂类A
static class ConcreteFactoryA implements IFactory{
public IProductA makeProductA() {
return new ConcreteProductAWithFamilyA();
}
public IProductB makeProductB() {
return new ConcreteProductBWithFamilyA();
}
}
//具体工厂类B
static class ConcreteFactoryB implements IFactory{
public IProductA makeProductA() {
return new ConcreteProductAWithFamilyB();
}
public IProductB makeProductB() {
return new ConcreteProductBWithFamilyB();
}
}
}
3 使用具象鞋厂模式支持产品扩充
我们来看一个具体的业务场景,并且用代码来实现。还是以网路课程为例,一般课程研制会有一定的标准,每个课程除了要提供课程的录播视频,还要提供老师的课堂笔记。相当于现今的业务变更为同一个课程不单纯是一个课程信息,要同时包含录播视频、课堂笔记,甚至要提供源码能够构成一个完整的课程。首先在产品等级中降低两个产品:录播视频IVideo和课堂笔记INote。 IVideo插口的代码如下。
public interface IVideo {
void record();
}
INote插口的代码如下。
public interface INote {

void edit();
}
然后创建一个具象鞋厂CourseFactory类。
/**
* 抽象工厂是用户的主入口
* 在Spring中应用得最为广泛的一种设计模式
* 易于扩展
* Created by Tom
*/
public abstract class CourseFactory {
public void init(){
System.out.println("初始化基础数据");
}
protected abstract INote createNote();
protected abstract IVideo createVideo();
}
接下来创建Java产品族,Java视频JavaVideo类的代码如下。
public class JavaVideo implements IVideo {
public void record() {
System.out.println("录制Java视频");
}
}
扩展产品等级Java课堂笔记JavaNote类。
public class JavaNote implements INote {
public void edit() {
System.out.println("编写Java笔记");
}
}
创建Java产品族的具体鞋厂JavaCourseFactory。
public class JavaCourseFactory extends CourseFactory {
public INote createNote() {
super.init();
return new JavaNote();
}
public IVideo createVideo() {
super.init();
return new JavaVideo();
}
}
随后创建Python产品族,Python视频PythonVideo类的代码如下。
public class PythonVideo implements IVideo {
public void record() {
System.out.println("录制Python视频");
}
}
扩展产品等级Python课堂笔记PythonNote类。
public class PythonNote implements INote {
public void edit() {
System.out.println("编写Python笔记");
}
}
创建Python产品族的具体鞋厂PythonCourseFactory。
public class PythonCourseFactory implements CourseFactory {
public INote createNote() {
return new PythonNote();
}
public IVideo createVideo() {
return new PythonVideo();
}
}
最后来看客户端调用代码。
public static void main(String[] args) {
JavaCourseFactory factory = new JavaCourseFactory();
factory.createNote().edit();
factory.createVideo().record();
}
上面代码完整地描述了Java课程和Python课程两个产品族,也描述了视频和笔记两个产品等级。抽象鞋厂非常完美、清晰地描述了这样一层复杂的关系。但是,不知道你们有没有发觉,如果再继续扩充产品等级,将源码Source也加入课程中,则代码从具象鞋厂到具体鞋厂要全部调整,这或许不符合开闭原则。
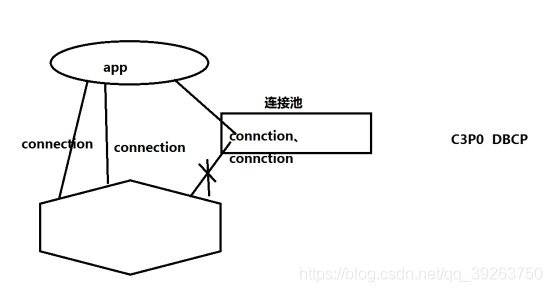
4 使用具象鞋厂模式构建数据库连接池
还是演示课堂开始的JDBC操作案例,我们每次操作都须要重新创建数据库联接。其实每次创建都十分花费性能,消耗业务调用时间。我们使用具象鞋厂模式,将数据库联接预先创建好,放到容器中缓存着,当业务调用时就只需现取现用。我们来看代码。 Pool抽象类的代码如下。
/**
* 自定义连接池getInstance()返回POOL唯一实例,第一次调用时将执行构造函数
* 构造函数Pool()调用驱动装载loadDrivers()函数;
* 连接池创建createPool()函数,loadDrivers()装载驱动
* createPool()创建连接池,getConnection()返回一个连接实例,
* getConnection(long time)添加时间限制
* freeConnection(Connection con)将con连接实例返回连接池,getnum()返回空闲连接数
* getnumActive()返回当前使用的连接数
*
* @author Tom
*
*/
public abstract class Pool {
public String propertiesName = "connection-INF.properties";
private static Pool instance = null; //定义唯一实例
/**
* 最大连接数
*/
protected int maxConnect = 100; //最大连接数
/**
* 保持连接数
*/
protected int normalConnect = 10; //保持连接数
/**
* 驱动字符串
*/
protected String driverName = null; //驱动字符串
/**
* 驱动类
*/
protected Driver driver = null; //驱动变量
/**
* 私有构造函数,不允许外界访问
*/
protected Pool() {
try
{
init();
loadDrivers(driverName);
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 初始化所有从配置文件中读取的成员变量
*/
private void init() throws IOException {
InputStream is = Pool.class.getResourceAsStream(propertiesName);
Properties p = new Properties();
p.load(is);
this.driverName = p.getProperty("driverName");
this.maxConnect = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("maxConnect"));
this.normalConnect = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("normalConnect"));
}
/**
* 装载和注册所有JDBC驱动程序
* @param dri 接收驱动字符串
*/
protected void loadDrivers(String dri) {
String driverClassName = dri;
try {
driver = (Driver) Class.forName(driverClassName).newInstance();
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
System.out.println("成功注册JDBC驱动程序" + driverClassName);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("无法注册JDBC驱动程序:" + driverClassName + ",错误:" + e);
}
}
/**
* 创建连接池
*/
public abstract void createPool();
/**
*
*(单例模式)返回数据库连接池Pool的实例
*
* @param driverName 数据库驱动字符串
* @return
* @throws IOException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws InstantiationException
*/
public static synchronized Pool getInstance() throws IOException,
InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
if (instance == null) {
instance = (Pool) Class.forName("org.e_book.sqlhelp.Pool").newInstance();
}
return instance;
}
/**
* 获得一个可用的连接,如果没有,则创建一个连接,并且小于最大连接限制
* @return
*/
public abstract Connection getConnection();
/**
* 获得一个连接,有时间限制
* @param time 设置该连接的持续时间(以毫秒为单位)
* @return
*/
public abstract Connection getConnection(long time);
/**
* 将连接对象返回连接池
* @param con 获得连接对象
*/
public abstract void freeConnection(Connection con);
/**
* 返回当前空闲的连接数
* @return
*/
public abstract int getnum();
/**
* 返回当前工作的连接数
* @return
*/
public abstract int getnumActive();
/**
* 关闭所有连接,撤销驱动注册(此方法为单例方法)
*/
protected synchronized void release() {
//撤销驱动
try {
DriverManager.deregisterDriver(driver);
System.out.println("撤销JDBC驱动程序 " + driver.getClass().getName());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out
.println("无法撤销JDBC驱动程序的注册:" + driver.getClass().getName());
}
}
}
DBConnectionPool数据库连接池的代码如下。
/**
* 数据库连接池管理类
* @author Tom
*
*/
public final class DBConnectionPool extends Pool {
private int checkedOut; //正在使用的连接数
/**
* 存放产生的连接对象容器
*/
private Vector freeConnections = new Vector();
//存放产生的连接对象容器
private String passWord = null; //密码
private String url = null; //连接字符串
private String userName = null; //用户名
private static int num = 0; //空闲连接数
private static int numActive = 0; //当前可用的连接数
private static DBConnectionPool pool = null; //连接池实例变量
/**
* 产生数据连接池
* @return
*/
public static synchronized DBConnectionPool getInstance()
{
if(pool == null)
{
pool = new DBConnectionPool();
}
return pool;
}
/**
* 获得一个数据库连接池的实例
*/
private DBConnectionPool() {
try
{
init();
for (int i = 0; i < normalConnect; i++) { //初始normalConn个连接
Connection c = newConnection();

if (c != null) {
freeConnections.addElement(c); //往容器中添加一个连接对象
num++; //记录总连接数
}
}
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 初始化
* @throws IOException
*/
private void init() throws IOException
{
InputStream is = DBConnectionPool.class.getResourceAsStream(propertiesName);
Properties p = new Properties();
p.load(is);
this.userName = p.getProperty("userName");
this.passWord = p.getProperty("passWord");
this.driverName = p.getProperty("driverName");
this.url = p.getProperty("url");
this.driverName = p.getProperty("driverName");
this.maxConnect = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("maxConnect"));
this.normalConnect = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("normalConnect"));
}
/**
* 如果不再使用某个连接对象,则可调此方法将该对象释放到连接池
* @param con
*/
public synchronized void freeConnection(Connection con) {
freeConnections.addElement(con);
num++;
checkedOut--;
numActive--;
notifyAll(); //解锁
}
/**
* 创建一个新连接
* @return
*/
private Connection newConnection() {
Connection con = null;
try {
if (userName == null) { //用户、密码都为空
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
} else {
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, passWord);
}
System.out.println("连接池创建一个新的连接");
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("无法创建这个URL的连接" + url);
return null;
}
return con;
}
/**
* 返回当前空闲的连接数
* @return
*/
public int getnum() {
return num;
}
/**
* 返回当前可用的连接数
* @return
*/
public int getnumActive() {
return numActive;
}
/**
* (单例模式)获取一个可用连接
* @return
*/
public synchronized Connection getConnection() {
Connection con = null;
if (freeConnections.size() > 0) { //还有空闲的连接
num--;
con = (Connection) freeConnections.firstElement();
freeConnections.removeElementAt(0);
try {
if (con.isClosed()) {
System.out.println("从连接池删除一个无效连接");
con = getConnection();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("从连接池删除一个无效连接");
con = getConnection();
}
//没有空闲连接且当前连接小于最大允许值,若最大值为0,则不限制
} else if (maxConnect == 0 || checkedOut
}
if (con != null) { //当前连接数加1
checkedOut++;
}
numActive++;
return con;
}
/**
* 获取一个连接,并加上等待时间限制,时间为毫秒
* @param timeout 接受等待时间(以毫秒为单位)
* @return
*/
public synchronized Connection getConnection(long timeout) {
long startTime = new Date().getTime();
Connection con;
while ((con = getConnection()) == null) {
try {
wait(timeout); //线程等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if ((new Date().getTime() - startTime) >= timeout) {
return null; //如果超时,则返回
}
}
return con;
}
/**
* 关闭所有连接
*/
public synchronized void release() {
try {
//将当前连接赋值到枚举中
Enumeration allConnections = freeConnections.elements();
//使用循环关闭连接池中的所用连接
while (allConnections.hasMoreElements()) {
//如果此枚举对象至少还有一个可提供的元素,则返回此枚举的下一个元素
Connection con = (Connection) allConnections.nextElement();
try {
con.close();
num--;
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("无法关闭连接池中的连接");
}
}
freeConnections.removeAllElements();
numActive = 0;
} finally {
super.release();
}
}
/**
* 建立连接池
*/
public void createPool() {
pool = new DBConnectionPool();
if (pool != null) {
System.out.println("创建连接池成功");
} else {
System.out.println("创建连接池失败");
}
}
}
5 抽象鞋厂模式在Spring源码中的应用
在Spring中,所有鞋厂都是BeanFactory的泛型。通过对BeanFactory的实现,我们可以从Spring的容器访问Bean。根据不同的策略调用getBean()方法,从而获得具体对象。
public interface BeanFactory {
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
T getBean(String name, @Nullable Class requiredType) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
T getBean(Class requiredType) throws BeansException;
T getBean(Class requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
boolean containsBean(String name);
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, @Nullable Class typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBean DefinitionException;
@Nullable
Class getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
BeanFactory的泛型主要有ClassPathXmlApplicationContext、XmlWebApplicationContext、StaticWebApplicationContext、StaticPortletApplicationContext、GenericApplicationContext和Static ApplicationContext。在Spring中,DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了所有鞋厂的公共逻辑。
【推荐】Tom弹构架:收藏本文,相当于收藏一本“设计模式”的书

